All Packages Class Hierarchy This Package Previous Next Index
java.lang.Object | +----java.awt.GridBagLayout
GridBagLayout class is a flexible layout manager that aligns components vertically and horizontally, without requiring that the components be of the same size. Each GridBagLayout object maintains a dynamic rectangular grid of cells, with each component occupying one or more cells, called its display area. Each component managed by a grid bag layout is associated with an instance of GridBagConstraints that specifies how the component is laid out within its display area.
How a GridBagLayout object places a set of components depends on the GridBagConstraints object associated with each component, and on the minimum size and the preferred size of the components' containers.
To use a grid bag layout effectively, you must customize one or more of the GridBagConstraints objects that are associated with its components. You customize a GridBagConstraints object by setting one or more of its instance variables:
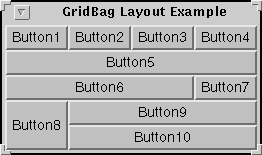
gridx, gridy gridx = 0, gridy = 0. Use GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE (the default value) to specify that the component be just placed just to the right of (for gridx) or just below (for gridy) the component that was added to the container just before this component was added. gridwidth, gridheight gridwidth) or column (for gridheight) in the component's display area. The default value is 1. Use GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER to specify that the component be the last one in its row (for gridwidth) or column (for gridheight). Use GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE to specify that the component be the next to last one in its row (for gridwidth) or column (for gridheight). fill GridBagConstraints.NONE (the default), GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL (make the component wide enough to fill its display area horizontally, but don't change its height), GridBagConstraints.VERTICAL (make the component tall enough to fill its display area vertically, but don't change its width), and GridBagConstraints.BOTH (make the component fill its display area entirely). ipadx, ipady (ipadx * 2) pixels (since the padding applies to both sides of the component). Similarly, the height of the component will be at least the minimum height plus (ipady * 2) pixels. insets anchor GridBagConstraints.CENTER (the default), GridBagConstraints.NORTH, GridBagConstraints.NORTHEAST, GridBagConstraints.EAST, GridBagConstraints.SOUTHEAST, GridBagConstraints.SOUTH, GridBagConstraints.SOUTHWEST, GridBagConstraints.WEST, and GridBagConstraints.NORTHWEST. weightx, weighty weightx) and column (weighty), all the components clump together in the center of their container. This is because when the weight is zero (the default), the GridBagLayout object puts any extra space between its grid of cells and the edges of the container. The following figure shows ten components (all buttons) managed by a grid bag layout:

Each of the ten components has the fill field of its associated GridBagConstraints object set to GridBagConstraints.BOTH. In addition, the components have the following non-default constraints:
weightx = 1.0 weightx = 1.0, gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER gridheight = 2, weighty = 1.0 gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER Here is the code that implements the example shown above:
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class GridBagEx1 extends Applet {
protected void makebutton(String name,
GridBagLayout gridbag,
GridBagConstraints c) {
Button button = new Button(name);
gridbag.setConstraints(button, c);
add(button);
}
public void init() {
GridBagLayout gridbag = new GridBagLayout();
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints();
setFont(new Font("Helvetica", Font.PLAIN, 14));
setLayout(gridbag);
c.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
c.weightx = 1.0;
makebutton("Button1", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button2", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button3", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
makebutton("Button4", gridbag, c);
c.weightx = 0.0; //reset to the default
makebutton("Button5", gridbag, c); //another row
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE; //next-to-last in row
makebutton("Button6", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
makebutton("Button7", gridbag, c);
c.gridwidth = 1; //reset to the default
c.gridheight = 2;
c.weighty = 1.0;
makebutton("Button8", gridbag, c);
c.weighty = 0.0; //reset to the default
c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row
c.gridheight = 1; //reset to the default
makebutton("Button9", gridbag, c);
makebutton("Button10", gridbag, c);
setSize(300, 100);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f = new Frame("GridBag Layout Example");
GridBagEx1 ex1 = new GridBagEx1();
ex1.init();
f.add("Center", ex1);
f.pack();
f.setSize(f.getPreferredSize());
f.show();
}
}
(x, y). target container using this grid bag layout. target container using this grid bag layout. protected static final int MAXGRIDSIZE
protected static final int MINSIZE
protected static final int PREFERREDSIZE
protected Hashtable comptable
protected GridBagConstraints defaultConstraints
protected GridBagLayoutInfo layoutInfo
public int columnWidths[]
public int rowHeights[]
public double columnWeights[]
public double rowWeights[]
public GridBagLayout()
public void setConstraints(Component comp, GridBagConstraints constraints)
public GridBagConstraints getConstraints(Component comp)
GridBagConstraints object is returned. protected GridBagConstraints lookupConstraints(Component comp)
GridBagConstraints object used by the layout mechanism. public Point getLayoutOrigin()
public int[][] getLayoutDimensions()
Most applications do not call this method directly.
public double[][] getLayoutWeights()
Most applications do not call this method directly.
public Point location(int x,
int y)
(x, y). Each cell is identified by its column index (ranging from 0 to the number of columns minus 1) and its row index (ranging from 0 to the number of rows minus 1). If the (x, y) point lies outside the grid, the following rules are used. The column index is returned as zero if x lies to the left of the layout, and as the number of columns if x lies to the right of the layout. The row index is returned as zero if y lies above the layout, and as the number of rows if y lies below the layout.
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)
public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp, Object constraints)
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
Most applications do not call this method directly.
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent)
target container using this grid bag layout. Most applications do not call this method directly.
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent)
target container using this grid bag layout. Most applications do not call this method directly.
public Dimension maximumLayoutSize(Container target)
public float getLayoutAlignmentX(Container parent)
public float getLayoutAlignmentY(Container parent)
public void invalidateLayout(Container target)
public void layoutContainer(Container parent)
GridBagLayout object. Most applications do not call this method directly.
public String toString()
protected GridBagLayoutInfo GetLayoutInfo(Container parent,
int sizeflag)
protected void AdjustForGravity(GridBagConstraints constraints, Rectangle r)
protected Dimension GetMinSize(Container parent,
GridBagLayoutInfo info)
protected void ArrangeGrid(Container parent)
All Packages Class Hierarchy This Package Previous Next Index